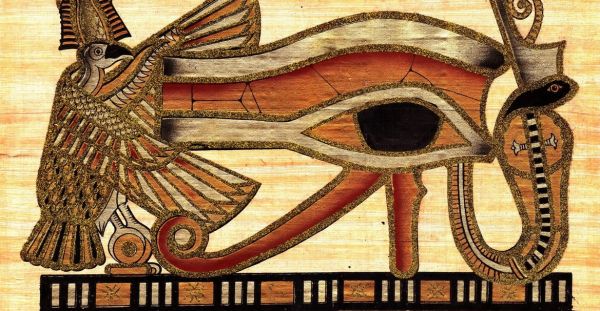
Meaning of the Egyptian Eye of Horus & Ra
The Eye of Horus, also known as the Egyptian Eye, is one of the most recognizable symbols of ancient Egypt. It has been featured in numerous depictions, from ancient temple walls to modern-day tattoos. But what does the Eye of Horus really mean, and why has it remained such an enduring symbol throughout history?
Meaning of the Eye of Horus
The Eye of Horus was a symbol of protection and power in ancient Egypt. It was believed to represent the god Horus, who was the son of Osiris and Isis, and was often depicted as a falcon-headed deity. The Eye of Horus was said to be the eye that Horus lost in battle with his uncle, Set, and was later restored by the god Thoth.
The Eye of Horus was also associated with the sun and moon, and was believed to have the power to heal and protect. It was often used in amulets and other talismans, and was believed to ward off evil spirits and protect the wearer from harm.
Symbolism of the Eye of Horus
The Eye of Horus is a complex symbol that has many layers of meaning. At its most basic level, it represents the eye that Horus lost in battle with Set, and the restoration of that eye by Thoth. This story was seen as a metaphor for the eternal struggle between good and evil, and the eventual triumph of good over evil.
The Eye of Horus was also believed to represent the concept of divine sight, or the ability to see beyond the physical world. It was seen as a symbol of enlightenment and wisdom, and was often associated with the all-seeing eye of Ra.
The All-Seeing Eye of Horus and Ra
The Eye of Horus is sometimes confused with the all-seeing eye of Ra, another ancient Egyptian symbol of power and magic. While the two symbols are similar, they have distinct differences in meaning. The all-seeing eye of Ra was associated with the sun god Ra, and was believed to represent his ability to see everything that was happening in the world.
It was often depicted as a human eye, with the sun disk and cobra of protection above it. The Eye of Horus, on the other hand, was associated with the god Horus and had a more complex meaning. While it was also seen as a symbol of divine sight, it was also associated with the concept of sacrifice and resurrection, as well as the eternal struggle between good and evil.
The Eye of Horus in Magic and Religion
The Eye of Horus was an important symbol in both magic and religion in ancient Egypt. It was often used in protective spells and rituals, and was believed to have the power to heal and protect. The Eye of Horus was also a symbol of the pharaoh's power and authority.
It was often depicted on the front of the pharaoh's crown, and was believed to give the pharaoh the power to see and understand all things. Today, the Eye of Horus continues to be an enduring symbol of power and magic. It is often used in jewelry and tattoos, and is seen as a symbol of protection and wisdom.
The Eye of Horus is an ancient Egyptian symbol that has endured for thousands of years. It represents the eternal struggle between good and evil, the power of divine sight, and the ability to heal and protect. Whether used in magic, religion, or simply as a symbol of personal power, the Eye of Horus continues to inspire and captivate people around the world.
Best Egypt Private Tours 2026
| Tour | Itinerary | Price |
|---|---|---|
| Egypt Solar Eclipse Tour | 9 Days | $ 6895 |
| All Inclusive Vacations Egypt | 10 Days | $ 1999 |
| Pyramids and Nile Cruise Holidays | 8 Days | $ 1595 |
| Luxury Egypt Tours with Nile Cruise | 12 Days | $ 2470 |
| Nile Cruise and Red Sea Stay | 12 Days | $ 2685 |
| Cairo Nile Cruise and Hurghada | 12 Days | $ 2065 |
| Package Trips to Egypt | 10 Days | $ 2065 |
| Egypt Honeymoon Packages | 10 Days | $ 3180 |
| Cairo and Nile Cruise for Disabled Travellers | 8 Days | $ 3075 |
| Egypt Wheelchair Accessible Tours | 10 Days | $ 2999 |
| Egypt and Kenya Tours | 15 Days | $ 6250 |
| Egypt and Dubai Tours | 8 Days | $ 999 |
| Cairo to Abu Simbel Tours | 8 Days | $ 1615 |
| Ancient Egypt Tours | 10 Days | $ 1999 |
| Luxury Dahabiya Nile Cruise and Cairo | 8 Days | $ 2945 |
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Eye of Ra lucky?
The Eye of Ra, an ancient Egyptian symbol associated with the sun god Ra, is generally considered a symbol of protection, royal power, and good health rather than luck in the modern sense. In ancient Egyptian mythology, the Eye of Ra was believed to ward off evil spirits and protect the pharaoh. It symbolizes the sun's life-giving and protective qualities.The interpretation of symbols can vary, and beliefs about luck are often subjective and cultural. In the context of ancient Egyptian beliefs, the Eye of Ra was not so much associated with luck as it was with divine protection and power.
Who is the god Ra in Egypt?
Ra, also spelled Re, is an ancient Egyptian sun god and one of the most important deities in the Egyptian pantheon. Ra is often depicted as a man with the head of a hawk, wearing a solar disk on his head. He is associated with the sun, light, warmth, and life.In ancient Egyptian mythology, Ra was considered the creator of the world and the ruler of the heavens. As the sun god, Ra was believed to travel across the sky during the day and journey through the underworld at night, emerging as the rising sun the next morning. Ra played a central role in Egyptian religious beliefs and was sometimes merged with other deities to form composite gods, such as Amun-Ra during the New Kingdom.Ra's importance declined over time as other gods gained prominence, but he remains a significant figure in the study of ancient Egyptian religion and mythology.
Is the Eye of Ra good or bad?
The Eye of Ra is a complex symbol in ancient Egyptian mythology and can represent both positive and negative aspects. Generally, it is associated with protection, royal power, and good health. However, there are two primary aspects of the Eye of Ra, often depicted as the left and right eyes:1. The Right Eye of Ra (the sun): This eye is associated with the sun god Ra and represents warmth, light, and life. It is considered a positive and protective symbol.2. The Left Eye of Ra (the lunar): This eye is associated with the goddess Sekhmet or Hathor and can be more ferocious. It is sometimes linked to destructive forces and is associated with the wrath of the goddess.The dual nature of the Eye of Ra symbolizes the balance of power, creation, and destruction in the Egyptian worldview. So, while it can be seen as both good and bad, it primarily serves protective and positive functions in ancient Egyptian beliefs.